Rods used to Straighten the Spine
 Scoliosis is a medical condition that affects the spine, causing it to curve sideways. While some cases of scoliosis are mild and require no treatment, others can cause significant discomfort and even lead to long-term health issues. In severe cases, doctors will recommend scoliosis surgery to correct the curvature of the spine and prevent further damage.
Scoliosis is a medical condition that affects the spine, causing it to curve sideways. While some cases of scoliosis are mild and require no treatment, others can cause significant discomfort and even lead to long-term health issues. In severe cases, doctors will recommend scoliosis surgery to correct the curvature of the spine and prevent further damage.
Doctors are successfully using metal rods to straighten the spine. These rods are used to straighten and stabilize the spine, allowing it to heal and return to its normal position. In this web page, we’ll explore the use of rods in scoliosis surgery, how they work, and the benefits and risks of this technique.
A Scoliosis Definition
Doctors recognize Scoliosis because they observe that the spine curves sideways, forming an S or C shape. This curvature can cause a range of symptoms, including back pain, muscle spasms, and limited mobility. In severe cases, scoliosis can lead to lung and heart problems, as the curvature of the spine can put pressure on these organs and interfere with their function.
Scoliosis can develop at any age, but it most commonly affects children and adolescents during growth spurts. Doctors do not know the exact cause of many scoliosis cases, but they believe it results from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. In some cases, scoliosis results from an underlying medical condition, such as muscular dystrophy or cerebral palsy.
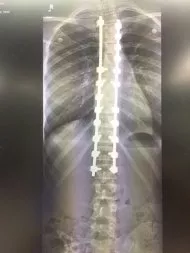
How are Rods Used in Scoliosis Surgery?
When scoliosis surgery becomes necessary, the doctors will straighten the spine to prevent further curvature. One technique that has been successfulluy used for this purpose is the insertion of rods into the spine. The procedure typically involves the following steps:
- An incision in the back to access the spine.
- The muscles surrounding the spine get moved aside to expose the vertebrae.
- Screws or hooks get inserted into the vertebrae at either end of the curve.
- A rod becomes attached to the screws or hooks and tightened to straighten the spine.
- Bone grafts get added to fuse the vertebrae together to maintain the spine’s new position.
The procedure typically takes several hours to complete and requires several days of hospitalization. Following surgery, patients will need to wear a brace for several months to ensure proper healing.
What are the Benefits for Scoliosis Surgery?
There are several benefits to using rods for scoliosis surgery, including:
- Improved spinal alignment: The use of rods allows for precise alignment of the spine, reducing curvature and improving overall spinal function.
- Reduced pain: In many cases, scoliosis surgery can significantly reduce or eliminate back pain associated with the condition.
- Improved lung and heart function: Straightening the spine can reduce pressure on the lungs and heart, improving their function and reducing the risk of complications.
- Faster recovery: Compared to traditional open surgery, the use of rods for scoliosis surgery can result in a faster recovery time and shorter hospital stay.
What are the Risks of Using Rods for Scoliosis Surgery?
While the use of rods for scoliosis surgery has many benefits, there are also some risks to consider, including:
- Infection: Like any surgical procedure, there is a risk of infection following scoliosis surgery. Patients receive antibiotics to reduce the risk of infection.
- Rod breakage: While rare, there is a risk of the rods breaking or becoming dislodged over time. This can require additional surgery to correct.
- Limited mobility: After surgery, some patients may experience limited mobility due to the fusion of the vertebrae. This can cause problems in younger patients who have not yet finished growing.
How Long Does it Take for a Surgery to Straighten the Spine
The length of time it takes to perform scoliosis surgery using rods to straighten the spine can vary depending on the specifics of the surgery, such as the severity of the curvature and the number of vertebrae involved. In general, scoliosis surgery using rods can take several hours to complete. The surgery typically involves making an incision in the back to access the spine and then attaching screws or hooks to the vertebrae at either end of the curve. A rod is then attached to the screws or hooks and tightened to straighten the spine. Bone grafts are added to fuse the vertebrae together and maintain the new position.
The exact length of the surgery will depend on the complexity of the case. In some cases, surgery can take as little as three or four hours, while in more complex cases, it may take six or more hours. After surgery, patients will need to spend several days in the hospital for monitoring and recovery. Following hospitalization, patients will need to wear a brace for several months to ensure proper healing. The length of time required for post-operative care can vary depending on the specifics of the surgery and the individual patient’s recovery process.
Make an Appointment with the Experts
The doctors and surgeons at the Southwest Scoliosis and Spine Institute are experts in straightening the spine. If you are experiencing back pain because of a curved spine, you should call and make an appointment as soon as possible. We have convenient offices in Dallas, Plano, and Frisco, Texas and we can see you very quickly.
____________________
Wiki How: Rods to straighten the spine
We’re here to help STOP THE PAIN
If your loved one suffers from scoliosis or another complex spine condition, hope exists. We can help. Call Southwest Scoliosis and Spine Institute at 214-556-0555 to make an appointment today.

Recent Comments